Fintech
The Reserve Bank of India sets out a fintech self-regulatory framework

The new structure aims to encourage cooperation, innovation and ethical behavior in the fintech sector…
The new structure aims to encourage cooperation, innovation and ethical behavior in the fintech sector.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) urges responsible innovation and growth within the country Indian fintech industry establishing a framework for the recognition of self-regulatory organizations (SROs). This framework, finalized in May 2024 after incorporating stakeholder feedback on a draft published earlier this year, outlines the characteristics, eligibility criteria, functions and responsibilities that SROs must comply with.
The RBI has recognized the immense potential of the fintech sector in revolutionizing the delivery of financial services in India, but has also raised concerns that the rapid growth of this sector needs a sound regulatory framework to ensure consumer protection, stability finance and responsible innovation. In a press release, the RBI highlighted the potential benefits of self-regulation, saying: “By pivoting towards a culture of self-governance, fintechs could proactively establish and adhere to industry standards and best practices. This approach could allow the sector to demonstrate its commitment to responsible conduct and innovation even in the absence of formal regulation.” The central bank believes that SROs play a vital role in fostering collaboration within the industry, enabling Fintech companies to collectively address challenges, foster an environment conducive to innovation and encourage a shared commitment to ethical business practices.
THE MULTI-FACED ROLE OF OADs
The RBI expects SROs to act as guardians of ethical conduct and responsible innovation in the Fintech sector. This multi-faceted role includes several key responsibilities:
Ensure compliance with standards and regulations
SROs must establish and enforce guidelines for consumer protection, security and data privacy. This includes ensuring that member fintech companies comply with industry standards and relevant legal and regulatory frameworks, with the SRO empowered to investigate and take disciplinary action against members who fail to comply with these standards.
Bridging the gap between industry and regulation
SROs are expected to act as a bridge between fintech companies and the RBI, facilitating communication by channeling industry concerns and recommendations to the central bank. Additionally, SROs can support the regulatory changes needed to support responsible innovation and growth in the fintech sector.
Innovation with equity
The new framework recognizes the importance of SROs promoting innovation equitably within the sector, stating that this can be achieved by establishing minimum eligibility criteria for membership that ensure representation from a broad range of fintech companies. SROs can also fill the skills gap by providing specialized knowledge and expertise to smaller entities, as well as offering guidance and contributing to capacity building through training programs. Maintaining a repository of industry data and trends can further serve as a valuable resource for research and policy making.
THE FUNCTIONS OF AN SRO: A DEEP DIVE
The RBI has outlined a comprehensive range of functions that SROs are mandated to perform. These functions are considered key to ensuring the responsible growth and stability of the fintech sector:
Standard settings
This involves establishing a code of conduct for advertising and marketing practices, ensuring responsible behavior by fintech companies, with SROs responsible for developing basic governance standards for the industry and specifying consequences for breaches of the established rules. Data collection and storage must be carried out in strict compliance with relevant data privacy regulations.
Supervision and enforcement
Creating a resilient framework for oversight and enforcement activities is critical, and SROs must develop and implement appropriate oversight mechanisms to effectively monitor members’ compliance with regulations and standards. Maintaining data confidentiality is critical and SROs are required to establish clear standards of conduct for their members. A defined range of disciplinary actions, including warnings, reprimands and expulsions, along with financial penalties, provides SROs with the tools needed to ensure compliance.
Development
Promoting a culture of compliance in the fintech sector is a key objective of SROs. According to the RBI, this can be achieved by facilitating the exchange of expertise and best practices among members, as well as organizing training programs to improve knowledge and skills. SROs are also expected to disseminate industry-specific information through various channels to raise awareness of developments, trends and best practices in the fintech industry. Furthermore, the framework encourages SROs to actively promote research and development through studies, surveys and discussions. To ensure inclusivity, SROs are tasked with extending guidance and support to smaller fintech entities, regardless of their member status.
Complaints redressal and dispute resolution
Establishing a robust framework for addressing customer complaints and resolving disputes efficiently, fairly and transparently is a key responsibility of SROs. This includes working to educate customers about fintech products and services, conducting regular assessments of the customer service standards offered by members, and implementing regular reviews of their complaint resolution framework to ensure its effectiveness.
ELIGIBILITY FOR SRO MEMBERSHIP
Membership of an SRO is primarily open to fintech companies that are not currently regulated by any financial sector regulator and are domiciled or registered in India. The framework also allows so-called “regulated entities” (excluding banks) to join. Participation is voluntary, and while membership fees may vary based on size and ability, the RBI has made it clear that the fee structure must be reasonable and non-discriminatory. The number of SROs to be recognized will be determined based on the nature and volume of applications received by the RBI.
REGISTERING AS A SRO: THE REQUIREMENTS
To be recognized as an SRO, an entity must meet the following stringent criteria set by the RBI:
Legal structure
The SRO must be incorporated as a not-for-profit company under Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013, to ensure that the organization operates for the benefit of the industry and not for private gain.
Equity diversity
To help ensure balanced and independent decision-making within the SRO, the RBI mandates diversification of the SRO’s shareholding, with no single entity holding more than 10% of the paid-up share capital.
Financial stability
The SRO must achieve a minimum net worth of INR 20 million (GBP 190,000) within one year of receiving recognition from the RBI or before commencing operations to ensure it has the resources to effectively discharge its responsibilities.
Infrastructure and capacity
The SRO must possess the necessary infrastructure and capabilities to effectively fulfill its responsibilities in a consistent manner, including an IT infrastructure that enables the implementation of technological solutions in a timely manner.
Management of damage to users
The framework requires SROs to establish effective systems for managing “user harm” resulting from practices such as fraud, mis-selling, unfair practices, unauthorized transactions or any other form of misconduct that harms consumers of financial services.
Operations abroad
SROs are prohibited from setting up entities or offices abroad without prior approval from the RBI. This ensures regulatory oversight and maintains control over SRO activities.
Fintech
US Agencies Request Information on Bank-Fintech Dealings

Federal banking regulators have issued a statement reminding banks of the potential risks associated with third-party arrangements to provide bank deposit products and services.
The agencies support responsible innovation and banks that engage in these arrangements in a safe and fair manner and in compliance with applicable law. While these arrangements may offer benefits, supervisory experience has identified a number of safety and soundness, compliance, and consumer concerns with the management of these arrangements. The statement details potential risks and provides examples of effective risk management practices for these arrangements. Additionally, the statement reminds banks of existing legal requirements, guidance, and related resources and provides insights that the agencies have gained through their oversight. The statement does not establish new supervisory expectations.
Separately, the agencies requested additional information on a broad range of arrangements between banks and fintechs, including for deposit, payment, and lending products and services. The agencies are seeking input on the nature and implications of arrangements between banks and fintechs and effective risk management practices.
The agencies are considering whether to take additional steps to ensure that banks effectively manage the risks associated with these different types of arrangements.
SUBSCRIBE TO THE NEWSLETTER
And get exclusive articles on the stock markets
Fintech
What changes in financial regulation have impacted the development of financial technology?

Exploring the complex landscape of global financial regulation, we gather insights from leading fintech leaders, including CEOs and finance experts. From the game-changing impact of PSD2 to the significant role of GDPR in data security, explore the four key regulatory changes that have reshaped fintech development, answering the question: “What changes in financial regulation have impacted fintech development?”
- PSD2 revolutionizes access to financial technology
- GDPR Improves Fintech Data Privacy
- Regulatory Sandboxes Drive Fintech Innovation
- GDPR Impacts Fintech Data Security
PSD2 revolutionizes access to financial technology
When it comes to regulatory impact on fintech development, nothing comes close to PSD2. This EU regulation has created a new level playing field for market players of all sizes, from fintech startups to established banks. It has had a ripple effect on other markets around the world, inspiring similar regulatory frameworks and driving global innovation in fintech.
The Payment Services Directive (PSD2), the EU law in force since 2018, has revolutionized the fintech industry by requiring banks to provide third-party payment providers (TPPs) with access to payment services and customer account information via open APIs. This has democratized access to financial data, fostering the development of personalized financial instruments and seamless payment solutions. Advanced security measures such as Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) have increased consumer trust, pushing both fintech companies and traditional banks to innovate and collaborate more effectively, resulting in a dynamic and consumer-friendly financial ecosystem.
The impact of PSD2 has extended beyond the EU, inspiring similar regulations around the world. Countries such as the UK, Australia and Canada have launched their own open banking initiatives, spurred by the benefits seen in the EU. PSD2 has highlighted the benefits of open banking, also prompting US financial institutions and fintech companies to explore similar initiatives voluntarily.
This has led to a global wave of fintech innovation, with financial institutions and fintech companies offering more integrated, personalized and secure services. The EU’s leadership in open banking through PSD2 has set a global standard, promoting regulatory harmonization and fostering an interconnected and innovative global financial ecosystem.
Looking ahead, the EU’s PSD3 proposals and Financial Data Access (FIDA) regulations promise to further advance open banking. PSD3 aims to refine and build on PSD2, with a focus on improving transaction security, fraud prevention, and integration between banks and TPPs. FIDA will expand data sharing beyond payment accounts to include areas such as insurance and investments, paving the way for more comprehensive financial products and services.
These developments are set to further enhance connectivity, efficiency and innovation in financial services, cementing open banking as a key component of the global financial infrastructure.
General Manager, Technology and Product Consultant Fintech, Insurtech, Miquido
GDPR Improves Fintech Data Privacy
Privacy and data protection have been taken to another level by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), forcing fintech companies to tighten their data management. In compliance with the GDPR, organizations must ensure that personal data is processed fairly, transparently, and securely.
This has led to increased innovation in fintech towards technologies such as encryption and anonymization for data protection. GDPR was described as a top priority in the data protection strategies of 92% of US-based companies surveyed by PwC.
Financial Expert, Sterlinx Global
Regulatory Sandboxes Drive Fintech Innovation
Since the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) pioneered sandbox regulatory frameworks in 2016 to enable fintech startups to explore new products and services, similar frameworks have been introduced in other countries.
This has reduced the “crippling effect on innovation” caused by a “one size fits all” regulatory approach, which would also require machines to be built to complete regulatory compliance before any testing. Successful applications within sandboxes give regulators the confidence to move forward and address gaps in laws, regulations, or supervisory approaches. This has led to widespread adoption of new technologies and business models and helped channel private sector dynamism, while keeping consumers protected and imposing appropriate regulatory requirements.
Co-founder, UK Linkology
GDPR Impacts Fintech Data Security
A big change in financial regulations that has had a real impact on fintech is the 2018 EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). I have seen how GDPR has pushed us to focus more on user privacy and data security.
GDPR means we have to handle personal data much more carefully. At Leverage, we have had to step up our game to meet these new rules. We have improved our data encryption and started doing regular security audits. It was a little tricky at first, but it has made our systems much more secure.
For example, we’ve added features that give users more control over their data, like simple consent tools and clear privacy notices. These changes have helped us comply with GDPR and made our customers feel more confident in how we handle their information.
I believe that GDPR has made fintech companies, including us at Leverage, more transparent and secure. It has helped build trust with our users, showing them that we take data protection seriously.
CEO & Co-Founder, Leverage Planning
Related Articles
Fintech
M2P Fintech About to Raise $80M

Application Programming Interface (API) Infrastructure Platform M2P Financial Technology has reached the final round to raise $80 million, at a valuation of $900 million.
Specifically, M2P Fintech, formerly known as Yap, is closing a new funding round involving new and existing investors, according to entrackr.com. The India-based company, which last raised funding two and a half years ago, previously secured $56 million in a round led by Insight Partners, earning a post-money valuation of $650 million.
A source indicated that M2P Fintech is ready to raise $80 million in this new funding round, led by a new investor. Existing backers, including Insight Partners, are also expected to participate. The new funding is expected to go toward enhancing the company’s technology infrastructure and driving growth in domestic and international markets.
What does M2P Fintech do?
M2P Fintech’s API platform enables businesses to provide branded financial services through partnerships with fintech companies while maintaining regulatory compliance. In addition to its operations in India, the company is active in Nepal, UAE, Australia, New Zealand, Philippines, Bahrain, Egypt, and many other countries.
Another source revealed that M2P Fintech’s valuation in this funding round is expected to be between USD 880 million and USD 900 million (post-money). The company has reportedly received a term sheet and the deal is expected to be publicly announced soon. The Tiger Global-backed company has acquired six companies to date, including Goals101, Syntizen, and BSG ITSOFT, to enhance its service offerings.
According to TheKredible, Beenext is the company’s largest shareholder with over 13% ownership, while the co-founders collectively own 34% of the company. Although M2P Fintech has yet to release its FY24 financials, it has reported a significant increase in operating revenue. However, this growth has also been accompanied by a substantial increase in losses.
Fintech
Scottish financial technology firm Aveni secures £11m to expand AI offering

By Gloria Methri
Today
- To come
- Aveni Assistance
- Aveni Detection
Artificial intelligence Financial Technology Aveni has announced one of the largest Series A investments in a Scottish company this year, amounting to £11 million. The investment is led by Puma Private Equity with participation from Par Equity, Lloyds Banking Group and Nationwide.
Aveni combines AI expertise with extensive financial services experience to create large language models (LLMs) and AI products designed specifically for the financial services industry. It is trusted by some of the UK’s leading financial services firms. It has seen significant business growth over the past two years through its conformity and productivity solutions, Aveni Detect and Aveni Assist.
This investment will enable Aveni to build on the success of its existing products, further consolidate its presence in the sector and introduce advanced technologies through FinLLM, a large-scale language model specifically for financial services.
FinLLM is being developed in partnership with new investors Lloyds Banking Group and Nationwide. It is a large, industry-aligned language model that aims to set the standard for transparent, responsible and ethical adoption of generative AI in UK financial services.
Following the investment, the team developing the FinLLM will be based at the Edinburgh Futures Institute, in a state-of-the-art facility.
Joseph Twigg, CEO of Aveniexplained, “The financial services industry doesn’t need AI models that can quote Shakespeare; it needs AI models that deliver transparency, trust, and most importantly, fairness. The way to achieve this is to develop small, highly tuned language models, trained on financial services data, and reviewed by financial services experts for specific financial services use cases. Generative AI is the most significant technological evolution of our generation, and we are in the early stages of adoption. This represents a significant opportunity for Aveni and our partners. The goal with FinLLM is to set a new standard for the controlled, responsible, and ethical adoption of generative AI, outperforming all other generic models in our select financial services use cases.”
Previous Article
Network International and Biz2X Sign Partnership for SME Financing
IBSi Daily News Analysis

SMBs Leverage Cloud to Gain Competitive Advantage, Study Shows
IBSi FinTech Magazine

- The Most Trusted FinTech Magazine Since 1991
- Digital monthly issue
- Over 60 pages of research, analysis, interviews, opinions and rankings
- Global coverage
subscribe now
-

 DeFi12 months ago
DeFi12 months agoDeFi Technologies Appoints Andrew Forson to Board of Directors
-

 Fintech12 months ago
Fintech12 months agoUS Agencies Request Information on Bank-Fintech Dealings
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoBlock Investors Need More to Assess Crypto Unit’s Earnings Potential, Analysts Say — TradingView News
-

 DeFi12 months ago
DeFi12 months agoSwitchboard Revolutionizes DeFi with New Oracle Aggregator
-

 DeFi12 months ago
DeFi12 months agoIs Zypto Wallet a Reliable Choice for DeFi Users?
-
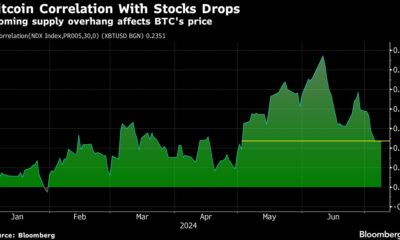
 News1 year ago
News1 year agoBitcoin and Technology Correlation Collapses Due to Excess Supply
-

 Fintech12 months ago
Fintech12 months agoWhat changes in financial regulation have impacted the development of financial technology?
-

 Fintech12 months ago
Fintech12 months agoScottish financial technology firm Aveni secures £11m to expand AI offering
-

 Fintech12 months ago
Fintech12 months agoScottish financial technology firm Aveni raises £11m to develop custom AI model for financial services
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoValueZone launches new tools to maximize earnings during the ongoing crypto summer
-

 Videos6 months ago
Videos6 months ago“Artificial intelligence is bringing us to a future that we may not survive” – Sco to Whitney Webb’s Waorting!
-

 DeFi1 year ago
DeFi1 year agoTON Network Surpasses $200M TVL, Boosted by Open League and DeFi Growth ⋆ ZyCrypto






